Ground Fault Sensors ensure safety in three-phase systems by detecting small current leaks that are caused by an imbalance in the current between phases.
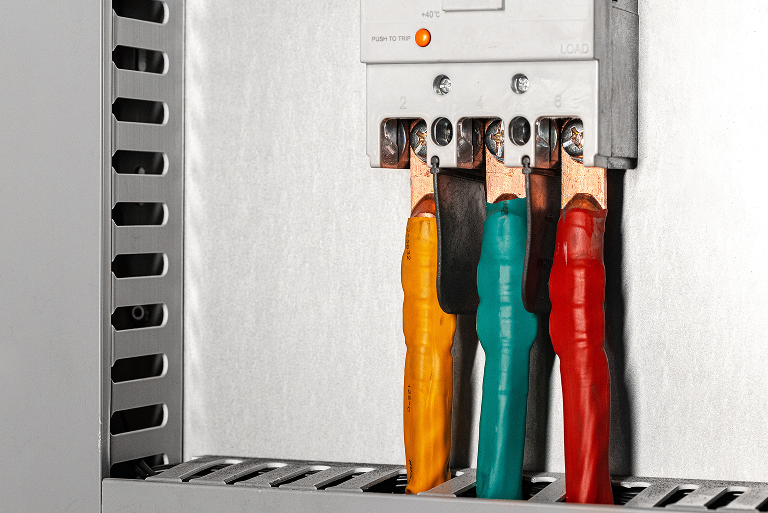
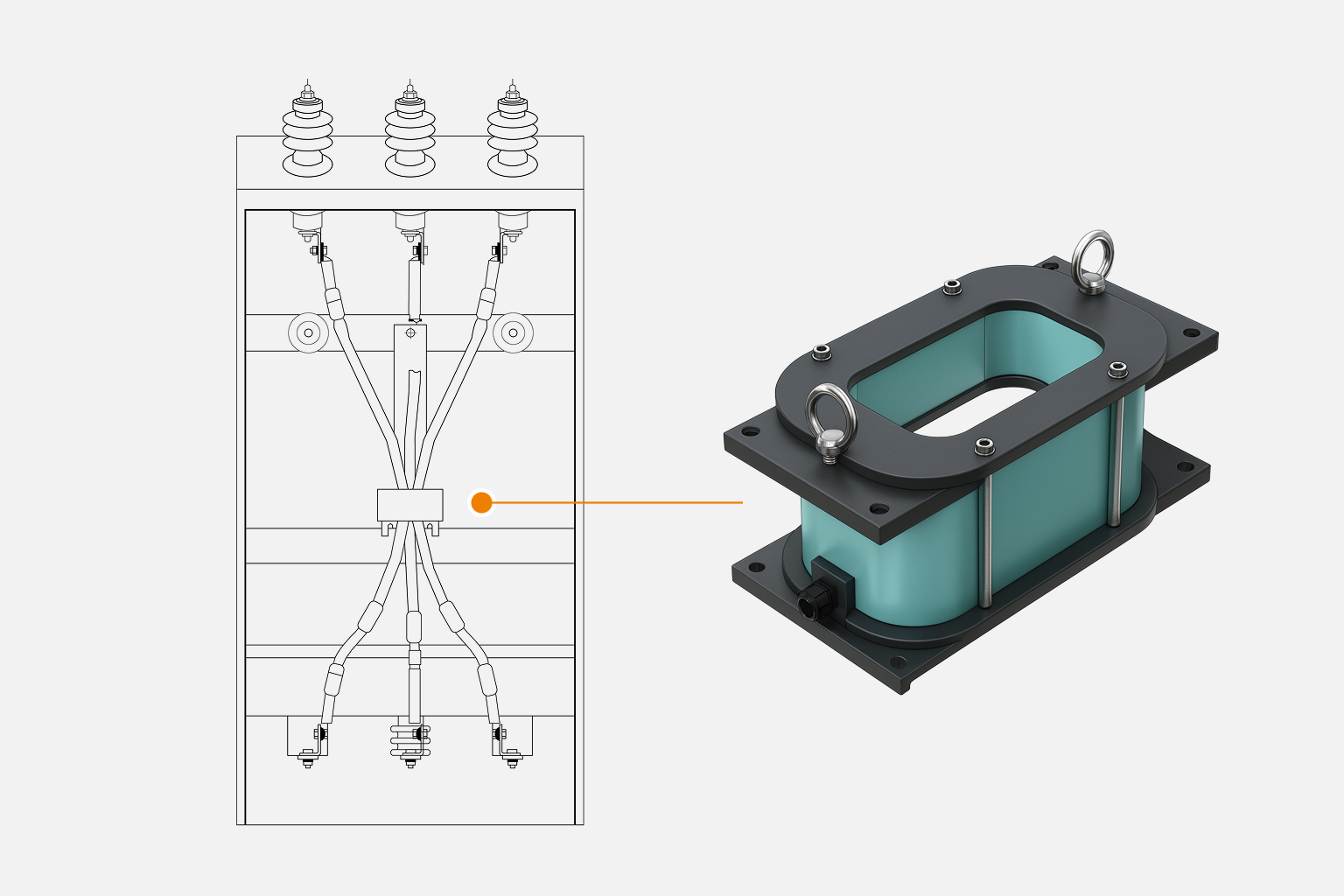

A ground fault sensor, commonly referred to as a zero-sequence current transformer, detects ground faults by measuring the vector sum of currents in all the phases and neutral conductors. Any imbalance produces a detectable zero-sequence current which is indicative of a ground fault.
These CTs are typically installed around the neutral conductor of a three-phase system or around all three phase conductors (plus the neutral, if applicable).
FEATURES
- Primary Current: up to 1000Amp
- Secondary Current: 1A, 5A or customized
- Relaying Class: up to C200 (or 10P20, 50VA)
- Short-time thermal current: up to 25kA (3s)
- Voltage Class: 600-720V
- Frequency: 50-60Hz
- IEEE C57.13, IEC 61869 compliant
- Large rectangular window (up to 25in of length)
© 2025 Falco Electronics. All rights reserved.
